

General Options

| **Multi-Language** | Enable multi-language project. If enabled, a combobox will appear on the top of the generated scripts
for user to select language. See Tools for selecting languages for the
multi-language project.
Important
|
| **Default Language** | Default language of the project. It must be compatible with Charset (see HTML Settings). Default is "en-US".
There is always one default language for a project. Only the English language file (english.en-US.xml) is shipped with PHPMaker. If your project is single language but you use another language, create a language file for your language (see Making Language Files), put it in the "languages" subfolder under the AppData folder (i.e. C:\Users\user\AppData\Roaming\PHPMaker2026\languages) and then select your default language using this combobox. If you enable Multi-Language, you must select one of the selected languages as the default language. |
| **File Upload** | 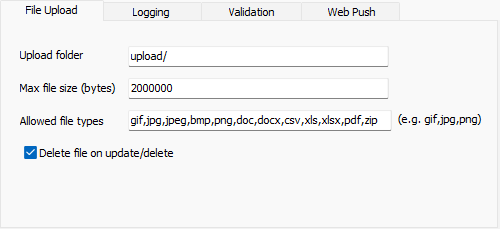
Upload folder - The global folder where the uploaded files resides. If you do not enter a specific folder for a file upload field in the Edit Tag panel of the Field Setup page, all the uploaded files will be put in this folder. Notes
Max File Size - Maximum file upload size in bytes. If <= 0, there is no checking on file size.
Notes File upload also depends on your PHP, web server and database
configuration:
Allowed file types - The allowed file extensions of the uploaded files. Separate the file extensions (without ".") by comma without space, e.g. gif,png,png. If blank, all file types are allowed. Delete file on update/delete - Option to delete the uploaded file when the field value is replaced, removed or if the record is deleted. Note
If Delete file on update/delete is enabled, the uploaded file will be deleted. If the
deleted record is a copied record, deleting the uploaded files will affect the original record. To
prevent such possible problem, enable Advanced Setting Create upload file on copy (see
Advanced Settings) to duplicate the uploaded file when copying a record.
|
| **Logging** | 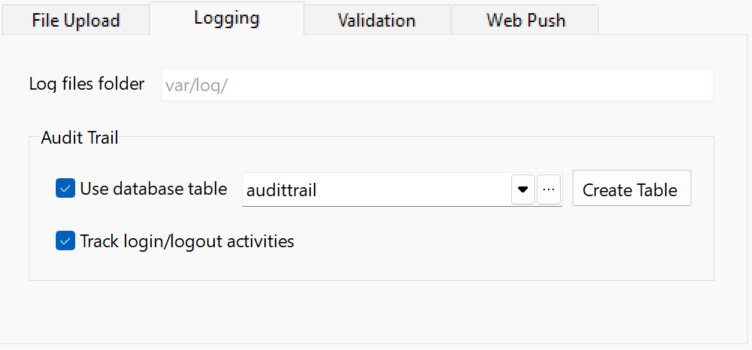
**Log file folder** - Deprecated The folder where the log file resides. By default, this uses `%kernel.logs_dir%`, which resolves to `%kernel.project_dir%/var/log`. This setting **cannot** be changed and does **not** automatically reflect changes made to the log directory in code, e.g. via `Kernel::getLogDir()`. Notes
Audit TrailUse database table - Log the activities in the specified table instead of log file. The table must have the following fields: (actual data types depend on database type)
You can create the database yourselves and select the table in the combobox, then click the [...] button to select the fields in your table. Alternatively, if you have not created the table yet, you can click Create Table to create the table and setup the table/fields. Track login/logout activities - If security feature is enabled, login/logout activities will also be logged. |
| **Validation** | 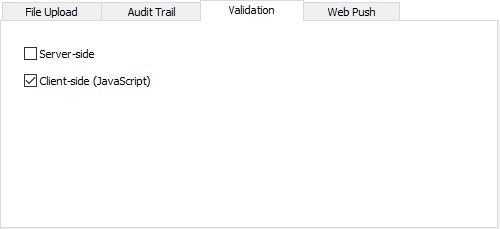
Server-side - Enable server-side form validation. Client-side (JavaScript) - Enable client-side form validation. Note If the available validation format in the
Edit Tag panel (see Field Setup) does not fulfil your requirements, you can
use your own server-side and/or client-side validation code using Server
Event and Client Scripts.
|
| **Web Push** | 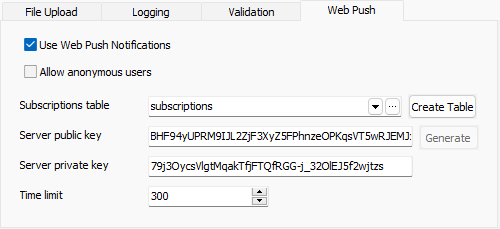
Use Web Push Notifications - Enable the Web Push Notificaiton feature.
You can create the database yourselves and select the table in the combobox, then click the [...] button to select the fields in your table. Alternatively, if you have not created the table yet, you can click Create Table button to create the table and setup the table/fields. Server public key - Web Push VAPID public key You can create the Server public/private key pairs by clicking the Generate button. Note The Generate button is only enabled if both keys are empty. If you want to generate again, clear both keys first. Time limit - Time limit (in seconds) for sending the Web Push Notification See Web Push Notification for more information. |
Page Options (Global)
The following page options are global for all tables. If you want different settings for a particular table, you can use table-specific options available in the Table Setup page.
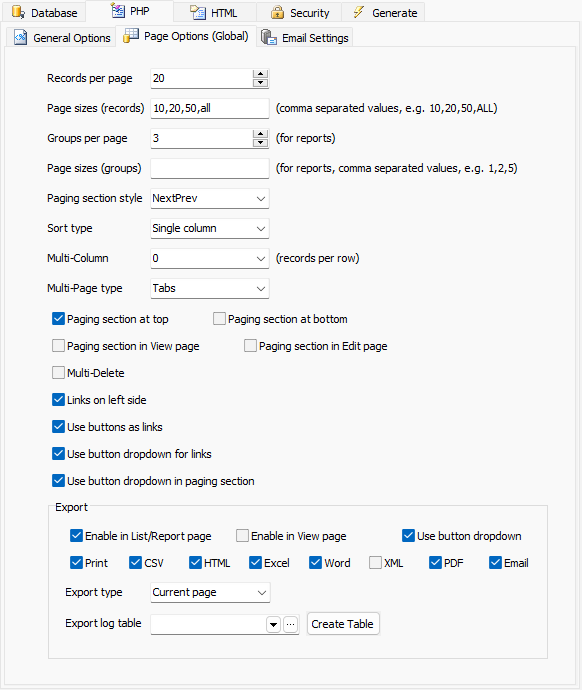
| **Records per page** | Number of records to be displayed in the list page of all tables. If blank or 0, default setting of 20 will be used. Not for reports. |
| **Page sizes (records)** | Number of records to be selected by user. Comma separated values,
e.g. 10,20,50,ALL. Not for reports.
Note "ALL" (without
quotes) is supported, other values must be integers.
|
| **Groups per page** | Number of groups to be displayed in reports. If blank or 0, default setting of 3 will be used. For reports only. |
| **Page sizes (groups)** | Number of groups to be selected by user. Comma separated values,
e.g. 1,2,3,5,ALL. For reports only.
Note "ALL" (without
quotes) is supported, other values must be integers.
|
| **Pager proximity** |
The number of page links to display around the current page.
Note
The old "PrevNext" and "Numeric" pagers are now integrated as one. If this setting is set to 0, it will regress to the PrevNext pager of previous version.
|
| **Sort type** | None, Single column or Multiple
column.
Note If Multiple column is
selected,
the List pages support multiple column sorting by Ctrl-clicking
the table header and clear sorting by Shift-clicking any table header.
|
| **Multiple column** | Show multiple records per row. Default is 0. This feature will only take effect if the value is > 0. Possible values: 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 12 |
| **Multi-Page type** | Default Multi-Page layout if Multi-Page is enabled. Possible values are:
|
| **Paging section at top** | Show the paging section at top (also applies to View page) |
| **Paging section at bottom** | Show the paging section at bottom (also applies to View page) |
| **Paging section in View page** | Show paging section in View page also |
| **Paging section in Edit page** | Show paging section in Edit page also |
| **Multi-Delete** | Show checkboxes in the list page for selecting multiple records to delete |
| **Links on left side** | Show the links in record row on the left instead of right |
| **Use buttons as links** | Show the links in record row as a button group instead of individual icons or links. |
| **Use button dropdown for links** | Show the links in record row as a button with dropdown menu instead of individual icons or links. |
| **Use button dropdown in paging section** | Show the links in paging section as buttons with dropdown menu instead of individual links. |
| **Export** | Enable export in List/Report page - allow export in List/Report pages
Enable export in View page - allow export in View pages also Use button dropdown - show the export links as a button with dropdown menu. Default is showing the export links as a row of icons. Print/CSV/HTML/Excel/Word/XML/PDF/Email - Records can be exported to Print (printer-friendly), CSV, HTML, Excel, Word, XML, PDF format or sent as HTML email content. Note The fields in printer friendly version are
same as in List/View page, while the fields in other format are determined by the Export setting of the
field in Field Setup page.
Export type - Determines which records to export. The follows are supported:
**Export log table** - For use with Export API which allows you to export snapshots from tables/views/reports and save them as physical files on server so they can be retrieved later. See [Export API](export.html) for details. Notes
Notes (Export to PDF)
|
| HTML/Print | Excel | Word | PhpSpreadsheet (for registered users) | PHPWord (for registered users) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| **Format** | HTML | HTML | HTML (NOT native) | HTML (NOT native) | Excel 5/2007 (native) | Word 2007 only (native) | |
| **Images** | |||||||
| **Charts (as images)** | |||||||
| **Custom Template** |
(Partially supported by Summary reports) |
(Partially supported by Summary reports) |
Email Settings
PHPMaker supports many features that can send emails. If you use these features, you'll need to specify a SMTP server.
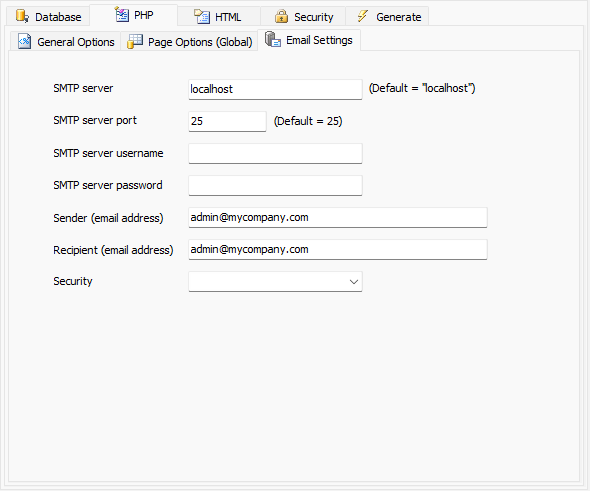
| **SMTP server** | The host name or IP of the SMTP server.
Note Some servers do not support
"localhost" as SMTP server, in such case you need to specify a valid SMTP server in the
network.
|
| **SMTP server port** | Port number of SMTP server. Default is 25. |
| **SMTP server username** | User name for SMTP server authentication. If your SMTP server does not require authentication, leave it blank. |
| **SMTP server password** | Password for SMTP server authentication. If your SMTP server does not require authentication, leave it blank. |
| **Sender (Email address)** | Email address of the sender of all emails |
| **Recipient (Email address)** | Email address of the recipient(s) for notification emails when a record is added/edited/deleted (if enabled, see Table Setup). If there are multiple recipients, separate them by comma. |
| **Security** | What kind of encryption to use on the SMTP connection. Possible values are: empty, `SSL` (use encryption) or `TLS` (use `STARTTLS`).
Notes
|
| **Test** | Press this button for testing your SMTP settings. A test email will be sent by Symfony built-in SMTP transport to the first **Recipient** you specified above. **Note** For testing Symfony built-in SMTP transport only, it does not support PHPMailer or 3rd party transports. |