

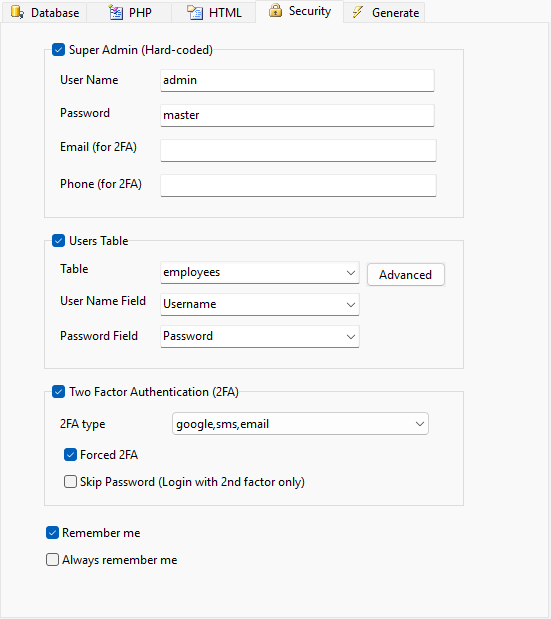
| Super Admin (Hard-Coded) | Super Admin user name and password |
| User Name | User Name of Super Admin |
| Password | Password of Super Admin |
| Email (for 2FA) | Email address of Super Admin for [Two factor Authentication](twofactorauth.html) |
| Phone (for 2FA) | Phone number (starting with "+" and country code) of Super Admin for [Two factor Authentication](twofactorauth.html) |
| Users Table | Users table for login name and password validation |
| Table | Existing table in database containing login name and password information |
| User Name Field | User name field in table used for authentication. This field MUST be of string type. |
| Password Field | Password field in table used for authentication. This field MUST be of string type. |
| Two factor authentication (2FA) | Enable Two Factor Authentication |
| 2FA type | Two factor authentication type:
|
| Forced 2FA | Force use of two factor authentication. If enabled, the user must use 2FA to login. |
| Skip Password (Login with 2nd factor only) | If enabled, the user will login without password and use only 2FA to login. Forced 2FA will also be enforced if this option is enabled. |
| Remember me | Once a user is authenticated, their credentials are typically stored in the session. This means that when the session ends they will be logged out and have to provide their login details again next time they wish to access the application. You can allow users to choose to stay logged in for longer than the session lasts using a cookie with this option. If enabled, an opt-in checkbox will be shown in the Login page to activate remember me, the remember me cookie will be created upon successful authentication. |
| Always remember me | Enable this setting to always activate the remember me system and not allow users to opt-out. When enabled, each successful authentication will produce a remember me cookie. |
Advanced Security
Advanced Security feature allows you to setup User ID and assign User Levels to users for **Authorization**, which refers to the process that determines what a user is able to do. After a user is [authenticated](authentication.html), the user is identified. The permission voter of the application can then use the user's User ID and User Levels to decide whether or not the user is allowed to perform some actions to tables and records. PHPMaker supports two types of security at different levels: - **User ID Security** secures data at **record level** - **User Level Security** secures data at **table level** They complements each other, they can work independently or together. Users get their User ID and User Level after login. Before login, a user's identity is unknown and the user is an **Anonymous User**. To setup, click the **Advanced** button under **Users Table**.User ID Security
User ID Security secures data at record level. Protected tables must have an User ID field for identifying which user a record belongs to. The User ID field names can be different in tables though. When User ID security is enabled, users can only access their own data.
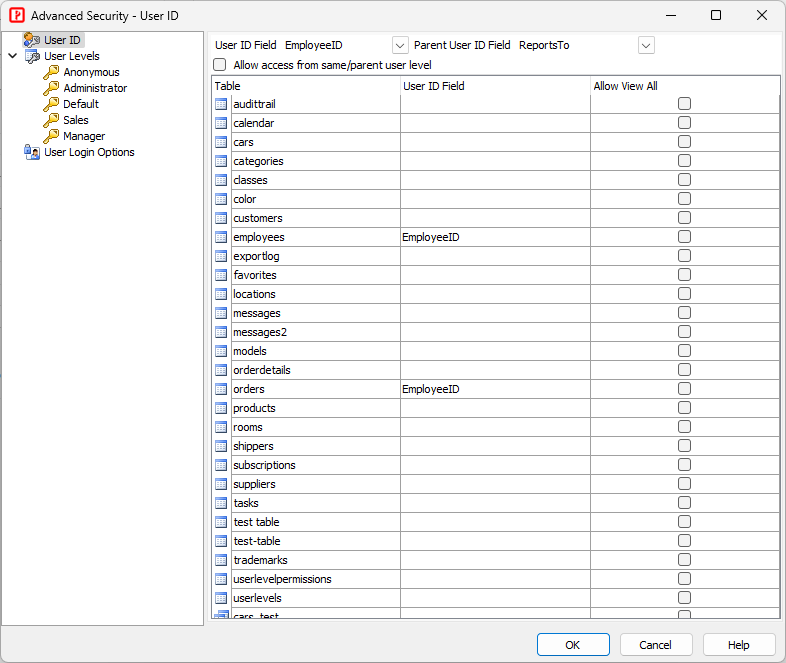
To setup User ID security for different tables/views,
User Level Security
User Level Security secures data at table level. Each user level is granted with specific permissions to tables in the database. There are 2 types of User Level Security: - **Static User Levels** - User Levels are defined in the project and cannot be changed with generated scripts - **Dynamic User Levels** - User Levels are stored in database and can be changed with generated scripts ###### User Level Hierarchy From v2025, user levels are hierarchical, each user level can have multiple sub user levels. A user level will automatically have all the permissions of sub user levels. For **Static User Levels**, the hierarchy is defined in the project. For **Dynamic User Levels**, the hierarchy is stored in the **Hierarchy Field** of the **User Level Table** (see below). ###### Static User Levels The user levels, hierarchy and the permissions are defined in this form. 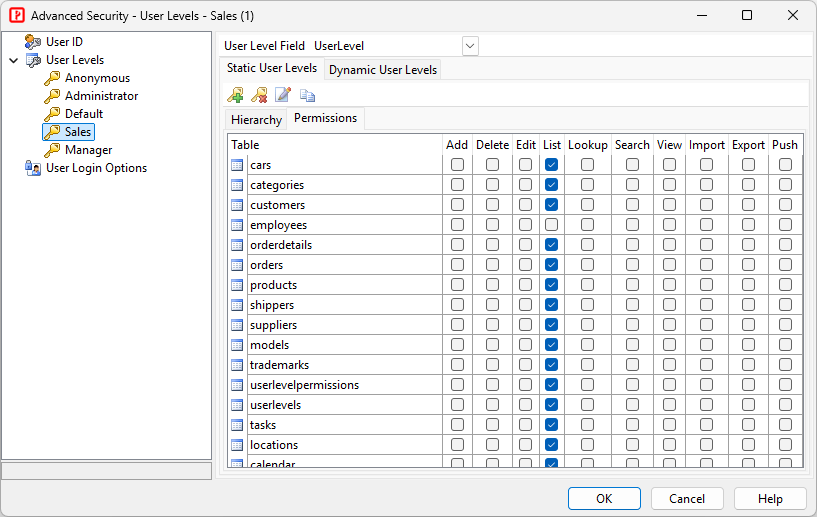 To setup static User Level security for different tables/views, 1. Click on **User Levels** in the left pane, 1. Select a field from your users table as the **User Level field**, 1. Click the **Static User Levels** tab, 1. Define your user levels, click  icon the add a user level and  icon to delete a user level. 1. Click the **Permissions** tab, select user levels in the left pane and set up permissions for each tables in the right pane. To setup static user level hierarchy, click the **Hierarchy** tab, set up the **Sub User Levels** for each user level. 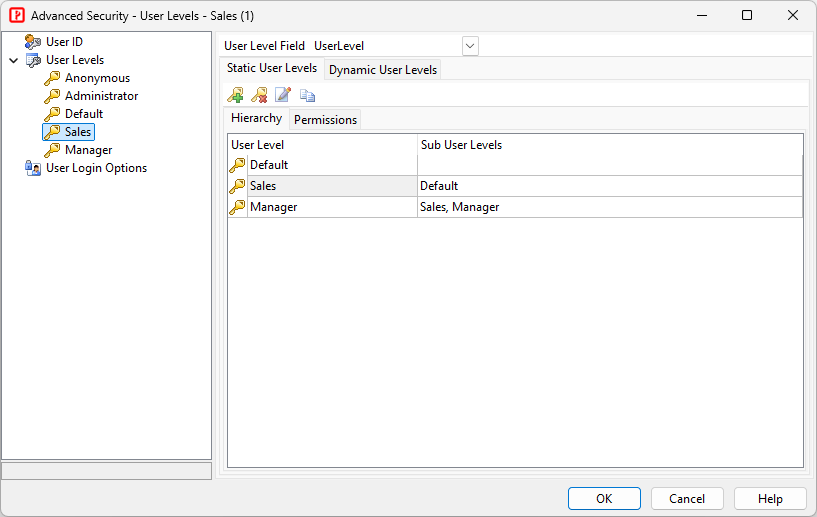 ###### Dynamic User Levels The user levels, hierarchy and permissions are stored in 2 database tables: **User Level Table** and **User Level Permission Table** 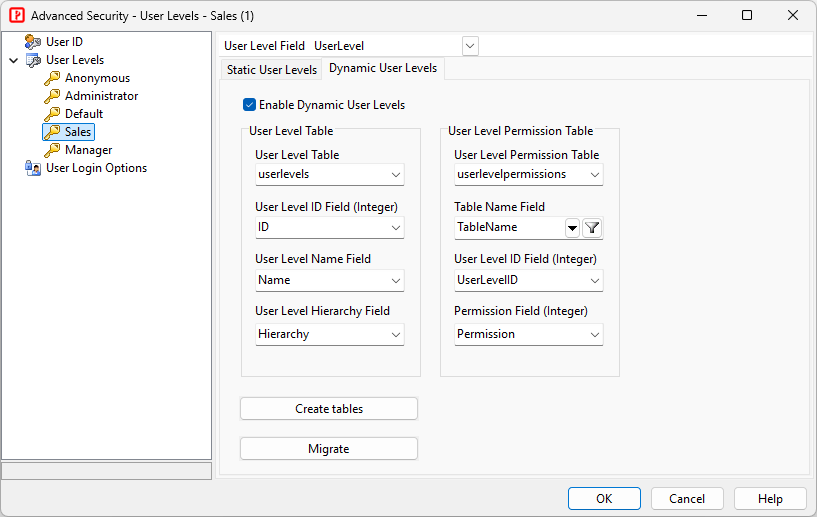 To setup dynamic User Level security for different tables/views, 1. Click on **User Levels** in the left pane, 2. Select a field from your users table as the **User Level field**, 3. Switch to the **Dynamic User Levels** tab, check **Enable Dynamic User Levels**, 4. Select your **User Level Table** and **User Level Permission Table** and the required fields.User Login Options
User Login Options allows you to create a complete user registration system for your website, with options
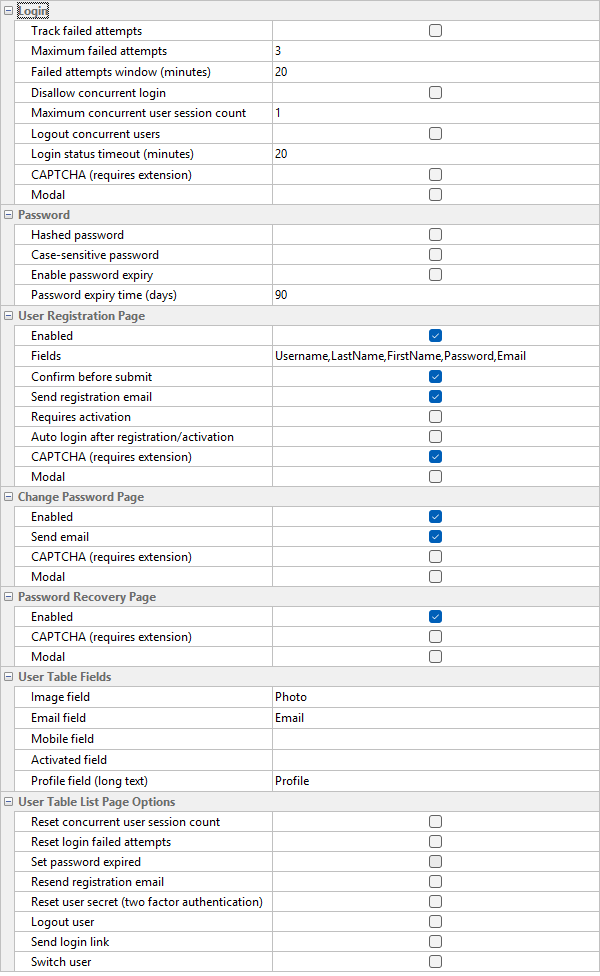
Login |
|
| Track failed attempts | If enabled, number of failed login attempts (invalid password) will be tracked. If exceeded, the user will be locked out and the password must be reset.
**Note** Login attempts are limited based on **Maximum failed attempts** and **Failed attempts window (minutes)**, see [Limiting Login Attempts](authentication.html?id=limiting-login-attempts) for details.
|
| Maximum failed attempts | The maximum number of failed login attempts. |
| Failed attempts window (minutes) | The time window, in minutes, during which failed password attempts are tracked. |
| Disallow concurrent login | If enabled, only one session is allowed for each user (except the hard-coded Administrator). If one user has already logged in, other users trying to login with the same username (and password) will be rejected.
Note Users are distinguished by Session ID as recognized by the web server. If you login again with your PC in another window of the same browser or in just another tab of your browser, you can still login. If you login again with another browser or another PC, the Session ID will be different and the login will be rejected.
|
| Maximum concurrent user session count | For use with Disallow concurrent login. By default only one session is allowed for each user. But you may want to give more than one chance to user so they will not be rejected after unexpected incidents such as a system crash.
Note Please be reminded that this option somewhat compromise the Disallow concurrent login feature. Use this option discreetly and always use the smallest possible value. |
| Logout concurrent users | For use with Disallow concurrent login. If enabled, when a new user login, other users who have already logged in with the same username will be logged out by the system. |
| Login status timeout (minutes) | The number of idle minutes after which the login status will be considered as logged out and login will be allowed again.
If a logged-in user does not explicitly log out (for example, close the browser directly), the user session is not closed and the user's login status will remain as "logged in". Attempts to login again will fail. This timeout setting ensures login will be allowed again after a period of idle time. |
| CAPTCHA (requires extension) | Optionally requires user to type letters or digits from a distorted image that appears on the screen..
Note Requires CAPTCHA extension, click Tools -> Extensions from the main menu to enable. Also see Third-party Tools. |
| Modal | Use modal dialog for login. |
Password |
|
| Enable password expiry | If enabled, user password will expire after a period of time (except the hard-coded Administrator password). |
| Password expiry time (days) | For use with Enable password expiry, user password will expire after the specified number of days. |
User Registration Page |
|
| Enabled | Generate user registration page and add a link in login page. |
| Fields | Select fields (from the user table) to show in the registration page. Click the [...] button the select the fields. |
| Confirm before submit | Display confirm page before submitting the registration |
| Send registration email | Optionally send email confirmation after registration |
| Requires activation | Optionally requires user to click an activation link in the email sent after registration to activate the user account.
Note Send email must be enabled for sending the email with activation link.
|
| Auto login after registration/activation | Optionally auto-login the user after registration or activation.
**Note** If **Requires activation** is enabled, the user is not activated yet after registration, auto login will be applied when the user clicks the activation link in the email. However, this option is not applicable if [LDAP authentication](tools.html?id=authentication-mode) mode is enabled.
|
| CAPTCHA (requires extension) | Optionally requires user to type letters or digits from a distorted image that appears on the screen..
Note Requires CAPTCHA extension, click Tools -> Extensions from the main menu to enable. Also see Third-party Tools.
|
| Modal | Use modal dialog for registration page. |
Change Password Page |
|
| Enabled | Generate change password page |
| Send email | Optional email confirmation after changing password |
| CAPTCHA (requires extension) | Optionally requires user to type letters or digits from a distorted image that appears on the screen.
Note Requires CAPTCHA extension, click Tools -> Extensions from the main menu to enable. Also see Third-party Tools. |
| Modal | Use modal dialog for change password page. |
Password Recovery Page |
|
| Enabled | Generate password recovery page to allow the user to request for a password reset. |
| CAPTCHA (requires extension) | Optionally requires user to type letters or digits from a distorted image that appears on the screen.
Note Requires CAPTCHA extension, click Tools -> Extensions from the main menu to enable. Also see Third-party Tools. |
| Modal | Use modal dialog for password recovery page. |
User Table Fields |
|
| Image field | Image field in user table used for showing user photo in sidebar |
| Email field | Email address field in user table used for sending email |
| Mobile field | Mobile phone field in user table used for sending SMS (used by 2FA) |
| Activated field | Email activated field in user table used for storing the status of user. A boolean field is recommended, although an integer field or a string field will also work. This field MUST be of boolean type.
Notes
|
| Profile field | A field for persisting all the additional user information. This field MUST be of long text type, e.g. ``TEXT`` or ``VARCHAR(65536)`` in MySQL; ``VARCHAR(65536)`` or ``VARCHAR(max)`` in SQL Server. This field is required if any of the follows are used:
|
User Table List Page Options |
|
| Reset concurrent user session count | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to reset the concurrent user session count of a user to 0 |
| Reset login failed attempts | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to reset the login failed attempts of a user to 0 |
| Set password expired | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to set the password of a user as expired |
| Resend registration email | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to resend the registration email to a user |
| Reset user secret (two factor authentication) | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to reset the user secret for two factor authentication. See Two Factor Authentication for details. |
| Logout user | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to force logout a logged in user. |
| Send login link | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to send login link to a user. |
| Switch user | If enabled, a new option is generated in the User Table list page for the administrator to switch to and impersonate a user. |
Also See
Tutorial - User ID Security
Tutorial - Static User Level Security
Tutorial - Dynamic User Level Security
Tutorial - User Registration System
Tutorial - Multi-Language Project Setup
Two Factor Authentication